Starting a business in Brazil can be an exciting yet challenging endeavor. Brazil, the largest economy in Latin America, offers diverse market opportunities, from technology to agriculture.
To understand, how to start a business in Brazil, one requires a strategic approach and a deep understanding of the market. This guide will take you through the step-by-step process of starting a profitable business in Brazil, providing key insights, statistics, and resources to help you succeed.
Why Choose Brazil To Start A Business?
Brazil is the largest economy in Latin America, with a GDP of approximately $2.1 trillion The country’s economy is diverse, with robust sectors in agriculture, mining, manufacturing, and services.
Recent trends show significant growth in technology, e-commerce, and renewable energy, making these sectors attractive for new businesses.
However, regional economic disparities mean that the market potential can vary significantly depending on the location. For instance, São Paulo is known for its bustling business environment, while the Northeastern regions may present different opportunities and challenges.
Types of Business Entities in Brazil
Selecting an appropriate business structure is an essential choice for any entrepreneur. In Brazil, the most common business structures include:
- Micro-Entrepreneur Individual (MEI): Suitable for small businesses with an annual revenue cap. It simplifies the registration process and tax obligations.
- EIRELI (Empresa Individual de Responsabilidade Limitada): An individual limited liability company.
- Limited Liability Company (LTDA): This is the most popular structure, offering limited liability to its owners. About 80% of new businesses in Brazil opt for LTDA.
- Corporation (SA): Ideal for larger businesses with more complex needs, allowing for greater capital accumulation through issuing shares.
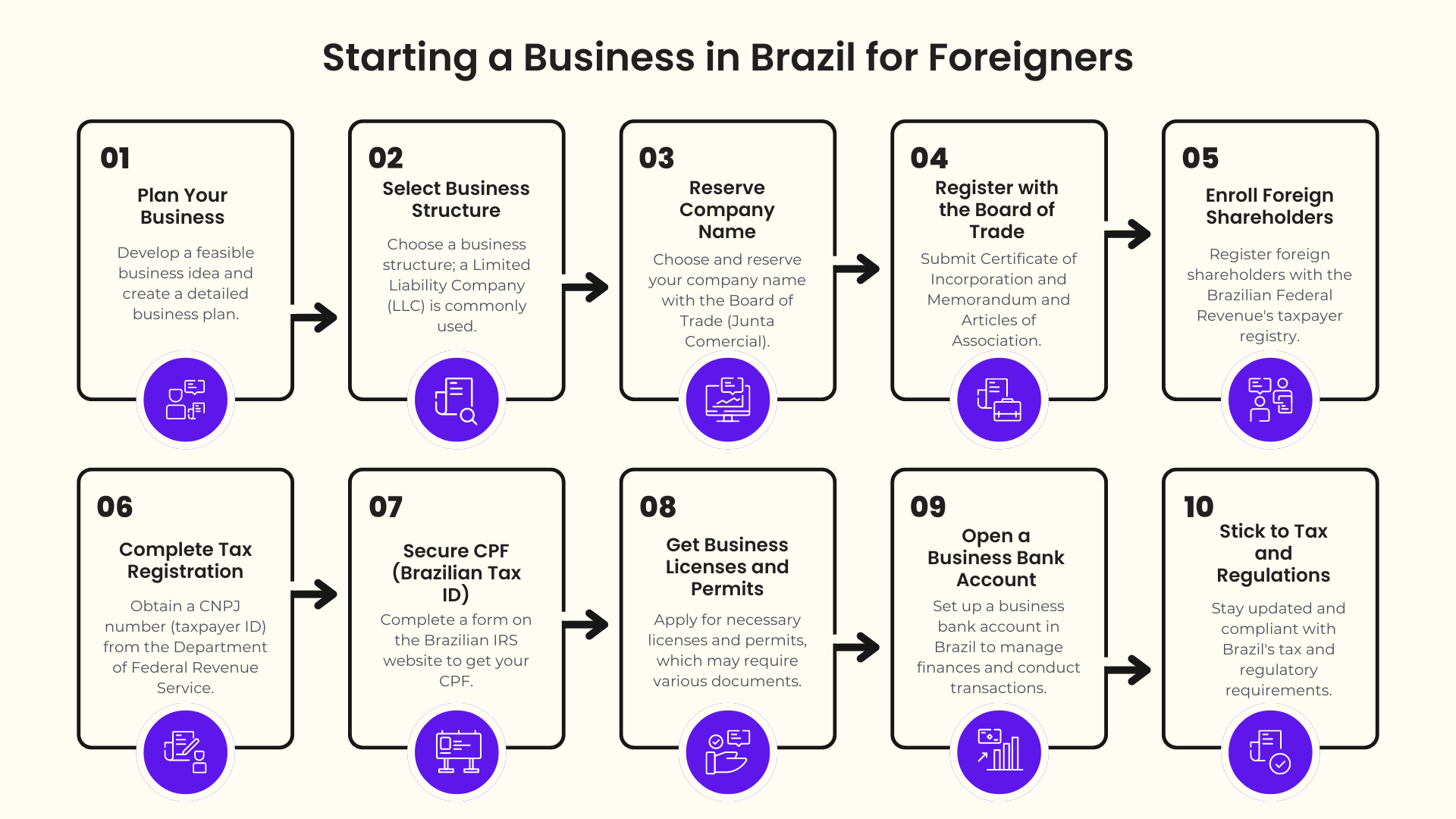
Legal Requirements and Registration Process
In Brazil, registering a business requires the following steps:
- Company Name Registration: Ensure the uniqueness of your business name with the Board of Trade (Junta Comercial).
- CNPJ Registration: Obtain the Brazilian company tax ID (CNPJ) from the Federal Revenue Service (Receita Federal).
- Articles of Incorporation: Draft and notarize the articles of incorporation or company bylaws.
- Municipal License: Obtain a municipal operation license (Alvará de Funcionamento) from the local city hall.
- Other Permits: Depending on your business activities, you may need additional licenses, such as environmental permits or health inspections.
Taxation and Compliance
Brazil has a complex tax system with various federal, state, and municipal taxes. For small and medium-sized businesses, the Simples Nacional regime simplifies taxation, allowing for a single tax payment covering federal, state, and municipal taxes.
Businesses not eligible for Simples Nacional must comply with taxes such as ICMS (goods and services tax), ISS (service tax), and IRPJ (corporate income tax).
Staying compliant with Brazilian tax regulations is crucial, and it is advisable to work with an experienced accountant or tax advisor to ensure all requirements are met.
Funding and Financial Planning
Financing Options for New Businesses
For aspiring business owners, obtaining capital can often be the largest obstacle. In Brazil, financing options include:
- Bank Loans and Credit Lines: Many banks in Brazil offer loans to new businesses, but the interest rates can be high, often exceeding 20% annually. It’s important to compare different financial institutions and their terms.
- Government Grants and Incentives: Programs like FINEP (Financiadora de Estudos e Projetos) provide funding for innovation-driven businesses, particularly in technology and research sectors.
- Private Investors: Venture capital and angel investors are increasingly active in Brazil, especially in sectors like fintech, e-commerce, and health tech. Networking and presenting a solid business plan are key to attracting private investment.
The Financial Cost of Starting a Business in Brazil
Setting up a company in Brazil involves a range of costs, typically between $3,000 and upwards of $10,000, although handling the process yourself may reduce expenses to under $500.
Key costs include registration fees paid to the Board of Trade, notary and legal fees for local services, and translation and apostille fees for documents not in Portuguese.
Understanding these costs can help you budget effectively and ensure a smoother business establishment process in Brazil.
Business Visa for Brazil
- Valid Passport: Ensure your passport is valid for at least six months beyond the date of your intended stay in Brazil.
- Visa Application Form: Complete the online visa application form thoroughly and accurately.
- Proof of Business Activities: Provide documentation such as an invitation letter from a Brazilian company, contracts, or business agreements to substantiate the purpose of your visit.
- Financial Resources: Prove that you have enough money to pay for all of your expenses while visiting Brazil.
- Visa Type: For US, Canadian, and Australian citizens, apply for the Visitor Visa (VIVIS).
 Creating a Financial Plan
Creating a Financial Plan
Creating a financial plan is vital for laying a solid foundation for your business. It not only helps you allocate resources efficiently but also prepares you for future challenges. Here’s a detailed breakdown of key components to include in your plan:
Startup Costs
Begin by listing all the initial expenses, including registration fees, legal costs, equipment, inventory, office space, and marketing expenses.
The initial expenses may differ significantly based on the type of business you operate. For instance, a retail business might require significant investment in inventory and a physical location, while a service-based business might have lower upfront costs.
Revenue Forecast
Projecting revenue involves estimating your sales based on market research, pricing strategies, and expected customer demand. Be realistic and consider various scenarios, including best-case and worst-case outcomes. Revenue projections should extend beyond the first year to include at least the first three to five years, providing a roadmap for growth and financial sustainability.
Expense Management
Identify both fixed costs (rent, utilities, salaries) and variable costs (materials, shipping, marketing). Keeping track of these expenses is crucial, as unchecked spending can quickly lead to cash flow problems.
Allocate funds for unexpected expenses, creating a buffer to ensure business continuity. Effective expense management can mitigate this risk and increase the chances of long-term success.
Currency Exchange and Managing Finances
Managing finances in Brazil comes with unique challenges, particularly due to the volatility of the Brazilian Real (BRL). Exchange rate fluctuations can significantly impact your business, especially if you’re dealing with international transactions.
- Hedge Against Currency Fluctuations: To protect against exchange rate volatility, consider using financial instruments such as forward contracts or options. These instruments allow you to lock in a specific exchange rate for future transactions, providing a hedge against unfavorable currency movements. Consulting with a financial advisor experienced in foreign exchange can help you implement these strategies effectively.
- Diversify Revenue Streams: Generating income in multiple currencies can reduce dependency on the BRL and mitigate currency risk. For example, if your business has the potential to export products or services, this can provide an additional revenue stream in a more stable currency.
- Open a Multicurrency Account: Some Brazilian banks and international financial institutions offer multicurrency accounts, enabling you to hold and manage funds in different currencies. This flexibility can simplify transactions with international clients and suppliers, reducing the impact of exchange rate fluctuations.
Hiring and Employment Laws
Brazilian labor laws are comprehensive and protect employee rights rigorously. Understanding these laws is crucial for hiring and managing staff:
- Employment Contracts: All employees must have a formal contract outlining job roles, salary, benefits, and conditions. Failure to provide a proper contract can result in legal disputes and penalties.
- 13th Salary: Employees in Brazil are entitled to a “13th salary,” which is an additional month’s pay that is usually given at the end of the year. This legal requirement must be factored into your annual payroll budget.
- Working Hours: In Brazil, an average workweek is forty-four hours long, or eight hours a day at most. Overtime regulations are strict, requiring additional pay for any hours worked beyond these limits.
When hiring in Brazil, it’s advisable to consult with a labor law expert to ensure compliance with these regulations. Offering competitive benefits and a positive work environment can help attract and retain top talent in a competitive market.
Marketing and Expanding Your Business
Marketing strategies in Brazil should be tailored to the local audience, leveraging digital platforms and localized content:
- Leverage Social Media: With over 70% of Brazilians actively using social media platforms like Instagram, Facebook, and WhatsApp these platforms are crucial for business promotion. Use interactive content, customer service channels, and targeted advertising to have direct conversations with your customers.
- Localize Your Content: Ensure your marketing materials are in Portuguese and culturally relevant. Localization extends beyond language translation; it involves adapting your content to resonate with Brazilian values, humor, and traditions.
- E-commerce Opportunities: Brazil’s e-commerce market is rapidly growing, presenting opportunities for businesses to expand online. Invest in a user-friendly website, mobile app, and secure payment gateway to cater to Brazil’s tech-savvy consumers.
Conclusion
Starting a business in Brazil requires careful planning, a deep understanding of the market, and adaptability to the local business environment. Every stage is essential for success, from figuring out the best corporate structure to negotiating the nuances of Brazilian regulations.
By leveraging this guide, conducting thorough research, and seeking local expertise, you can build a strong foundation for your business in Brazil. Embrace the opportunities this vibrant market offers and take the next step toward realizing your entrepreneurial ambitions.

