Começar um negócio no Brasil pode ser um empreendimento empolgante, mas desafiador.
O Brasil, a maior economia da América Latina, oferece diversas oportunidades de mercado, da tecnologia à agricultura.
Para entender como iniciar um negócio no Brasil, você precisa de uma abordagem estratégica e de um profundo conhecimento do mercado.
Este guia o guiará pelo processo passo a passo para iniciar um negócio lucrativo no Brasil, fornecendo as principais percepções, estatísticas e recursos para ajudá-lo a ter sucesso.
Por que escolher o Brasil para iniciar um negócio?
O Brasil é a maior economia da América Latina, com um PIB de aproximadamente US$ 2,1 trilhões. A economia do país é diversificada, com setores robustos na agricultura, mineração, manufatura e serviços.
Tendências recentes mostram um crescimento significativo em tecnologia, comércio eletrônico e energia renovável, tornando esses setores atraentes para novos negócios.
No entanto, as disparidades econômicas regionais significam que o potencial de mercado pode variar significativamente dependendo do local.
Por exemplo, São Paulo é conhecida por seu ambiente de negócios movimentado, enquanto as regiões do Nordeste podem apresentar oportunidades e desafios diferentes.
Tipos de entidades empresariais no Brasil
A seleção de uma estrutura de negócios adequada é uma escolha essencial para qualquer empreendedor.
No Brasil, as estruturas empresariais mais comuns incluem:
- Microempreendedor Individual (MEI): Adequado para pequenas empresas com um limite de receita anual.
Simplifica o processo de registro e as obrigações fiscais. - EIRELI (Empresa Individual de Responsabilidade Limitada): Uma empresa individual de responsabilidade limitada.
- Empresa de responsabilidade limitada (LTDA): Essa é a estrutura mais popular, oferecendo responsabilidade limitada a seus proprietários.
Cerca de 80% das novas empresas no Brasil optam pela LTDA. - Corporação (SA): Ideal para empresas maiores com necessidades mais complexas, permitindo maior acúmulo de capital por meio da emissão de ações.
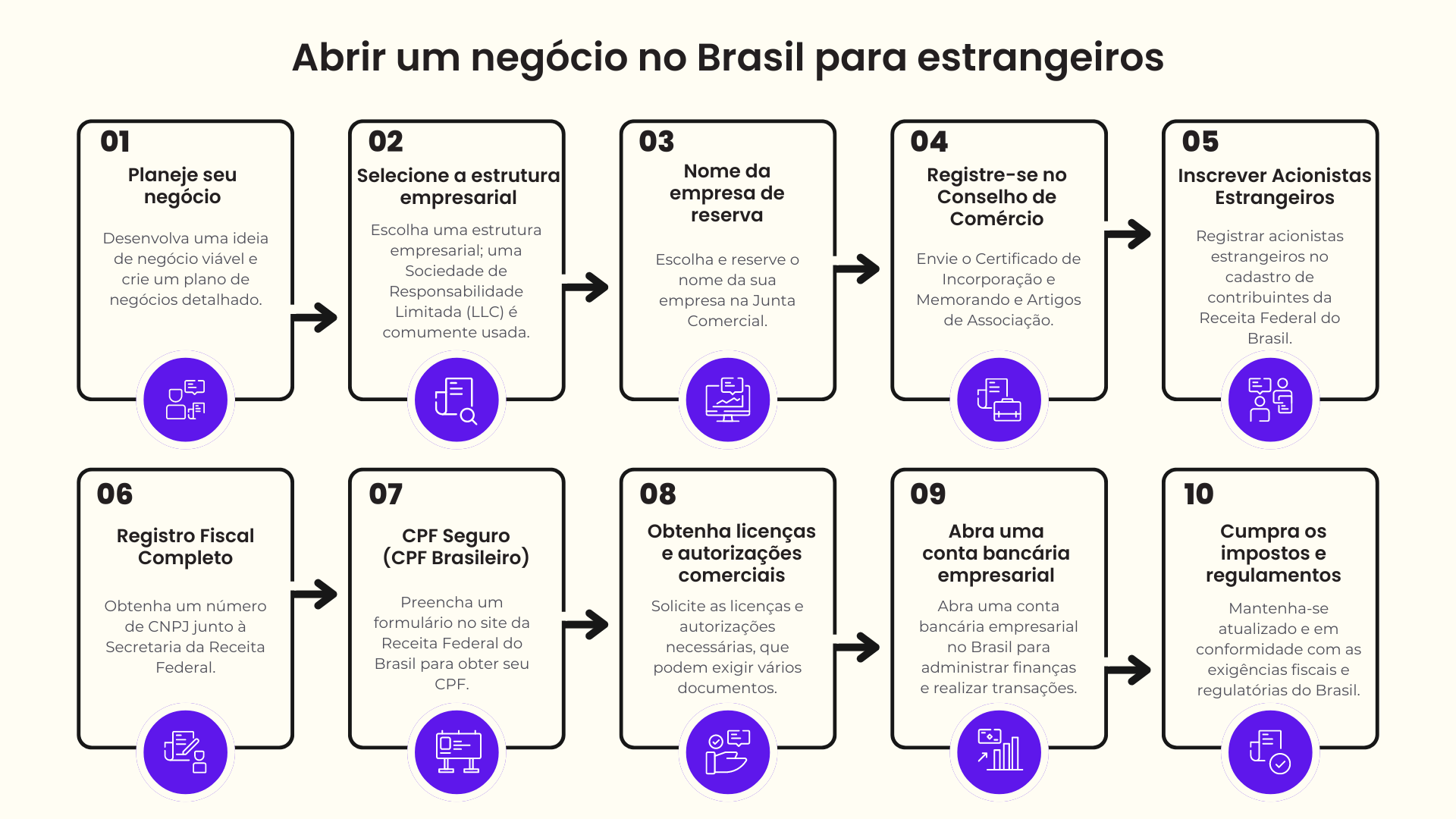
Requisitos legais e processo de registro
No Brasil, o registro de uma empresa requer as seguintes etapas:
- Registro do nome da empresa: Garanta a exclusividade do nome de sua empresa na Junta Comercial.
- Registro do CNPJ: Obtenha a identificação fiscal da empresa brasileira (CNPJ) junto à Receita Federal.
- Artigos de incorporação: Redigir e reconhecer em cartório os artigos de incorporação ou o estatuto da empresa.
- Licença municipal: Obtenha uma licença municipal de operação (Alvará de Funcionamento) na prefeitura local.
- Outras licenças: Dependendo das suas atividades comerciais, você pode precisar de licenças adicionais, como licenças ambientais ou inspeções sanitárias.
Tributação e conformidade
Brazil has a complex tax system with various federal, state, and municipal taxes. For small and medium-sized businesses, the Simples Nacional regime simplifies taxation, allowing for a single tax payment covering federal, state, and municipal taxes.
As empresas não qualificadas para o Simples Nacional devem cumprir com impostos como o ICMS (imposto sobre mercadorias e serviços), o ISS (imposto sobre serviços) e o IRPJ (imposto de renda de pessoa jurídica).
Manter-se em conformidade com as normas tributárias brasileiras é fundamental, e é aconselhável trabalhar com um contador ou consultor tributário experiente para garantir que todas as exigências sejam cumpridas.
Financiamento e planejamento financeiro
Opções de financiamento para novas empresas
Para os aspirantes a empresários, a obtenção de capital muitas vezes pode ser o maior obstáculo.
No Brasil, as opções de financiamento incluem:
- Empréstimos bancários e linhas de crédito: Muitos bancos no Brasil oferecem empréstimos para novas empresas, mas as taxas de juros podem ser altas, geralmente superiores a 20% ao ano.
É importante que você compare as diferentes instituições financeiras e seus termos. - Subsídios e incentivos do governo: Programas como a FINEP (Financiadora de Estudos e Projetos) fornecem financiamento para empresas voltadas para a inovação, especialmente nos setores de tecnologia e pesquisa.
- Investidores privados: Os investidores de capital de risco e anjos estão cada vez mais ativos no Brasil, especialmente em setores como fintech, comércio eletrônico e tecnologia da saúde.
O networking e a apresentação de um plano de negócios sólido são fundamentais para atrair investimentos privados.
O custo financeiro de abrir uma empresa no Brasil
A abertura de uma empresa no Brasil envolve uma série de custos, normalmente entre US$ 3.000 e mais de US$ 10.000, embora o fato de você mesmo cuidar do processo possa reduzir as despesas para menos de US$ 500.
Os principais custos incluem taxas de registro pagas à Junta Comercial, taxas de cartório e jurídicas para serviços locais e taxas de tradução e apostila para documentos que não estejam em português.
A compreensão desses custos pode ajudar você a fazer um orçamento eficaz e garantir um processo de estabelecimento de negócios mais tranquilo no Brasil.
Visto de negócios para o Brasil
- Passaporte válido: Certifique-se de que seu passaporte seja válido por pelo menos seis meses além da data em que você pretende permanecer no Brasil.
- Formulário de solicitação de visto: Preencha o formulário de solicitação de visto on-line de forma completa e precisa.
- Comprovação de atividades comerciais: Forneça documentação, como uma carta-convite de uma empresa brasileira, contratos ou acordos comerciais para comprovar o propósito de sua visita.
- Recursos financeiros: Comprove que você tem dinheiro suficiente para pagar todas as suas despesas durante a visita ao Brasil.
- Tipo de visto: Para cidadãos americanos, canadenses e australianos, solicite o Visto de Visitante (VIVIS).
 Criação de um plano financeiro
Criação de um plano financeiro
Criar um plano financeiro é vital para que você estabeleça uma base sólida para sua empresa.
Ele não apenas ajuda você a alocar recursos de forma eficiente, mas também o prepara para desafios futuros.
Aqui você encontra uma análise detalhada dos principais componentes que devem ser incluídos em seu plano:
Custos de inicialização
Comece listando todas as despesas iniciais, inclusive taxas de registro, custos legais, equipamentos, estoque, espaço de escritório e despesas de marketing.
As despesas iniciais podem diferir significativamente de acordo com o tipo de negócio que você opera.
Por exemplo, um negócio de varejo pode exigir um investimento significativo em estoque e um local físico, enquanto um negócio baseado em serviços pode ter custos iniciais mais baixos.
Previsão de receita
Projetar a receita envolve estimar suas vendas com base em pesquisas de mercado, estratégias de preços e demanda esperada dos clientes.
Seja realista e considere vários cenários, incluindo os melhores e os piores resultados.
As projeções de receita devem ir além do primeiro ano e incluir pelo menos os primeiros três a cinco anos, fornecendo um roteiro para o crescimento e a sustentabilidade financeira.
Gerenciamento de despesas
Identifique os custos fixos (aluguel, serviços públicos, salários) e os custos variáveis (materiais, remessa, marketing).
É fundamental manter o controle dessas despesas, pois gastos não controlados podem levar rapidamente a problemas de fluxo de caixa.
Alocar fundos para despesas inesperadas, criando uma reserva para garantir a continuidade dos negócios.
O gerenciamento eficaz de despesas pode reduzir esse risco e aumentar as chances de sucesso a longo prazo.
Câmbio de moedas e gerenciamento de finanças
A administração das finanças no Brasil apresenta desafios únicos, principalmente devido à volatilidade do real brasileiro (BRL).
As flutuações da taxa de câmbio podem afetar significativamente seus negócios, especialmente se você estiver lidando com transações internacionais.
- Proteção contra flutuações cambiais: Para se proteger contra a volatilidade da taxa de câmbio, considere o uso de instrumentos financeiros, como contratos a termo ou opções.
Esses instrumentos permitem que você fixe uma taxa de câmbio específica para transações futuras, proporcionando uma proteção contra movimentos desfavoráveis da moeda.
Consultar um consultor financeiro com experiência em câmbio pode ajudar você a implementar essas estratégias de forma eficaz. - Diversificar os fluxos de receita: A geração de receita em várias moedas pode reduzir a dependência do real e mitigar o risco cambial.
Por exemplo, se a sua empresa tiver o potencial de exportar produtos ou serviços, isso pode proporcionar um fluxo de receita adicional em uma moeda mais estável. - Abrir uma conta em várias moedas: Alguns bancos brasileiros e instituições financeiras internacionais oferecem contas em várias moedas, permitindo que você mantenha e gerencie fundos em diferentes moedas.
Essa flexibilidade pode simplificar as transações com clientes e fornecedores internacionais, reduzindo o impacto das flutuações da taxa de câmbio.
Leis de contratação e emprego
As leis trabalhistas brasileiras são abrangentes e protegem rigorosamente os direitos dos funcionários.
Entender essas leis é fundamental para a contratação e o gerenciamento da equipe:
- Contratos de trabalho: Todos os funcionários devem ter um contrato formal que descreva as funções, o salário, os benefícios e as condições do trabalho.
O não fornecimento de um contrato adequado pode resultar em disputas e penalidades legais. - 13º Salário: Os funcionários no Brasil têm direito a um “13º salário”, que é um mês adicional de pagamento que geralmente é dado no final do ano.
Essa exigência legal deve ser considerada em seu orçamento anual da folha de pagamento. - Horário de trabalho: No Brasil, uma semana de trabalho média é de quarenta e quatro horas, ou seja, no máximo oito horas por dia.
Os regulamentos sobre horas extras são rigorosos, exigindo pagamento adicional por qualquer hora trabalhada além desses limites.
Ao contratar no Brasil, é aconselhável que você consulte um especialista em direito trabalhista para garantir a conformidade com essas normas.
Oferecer benefícios competitivos e um ambiente de trabalho positivo pode ajudar a atrair e reter os melhores talentos em um mercado competitivo.
Marketing e expansão de seus negócios
As estratégias de marketing no Brasil devem ser adaptadas ao público local, aproveitando as plataformas digitais e o conteúdo localizado:
- Aproveite a mídia social: Com mais de 70% dos brasileiros usando ativamente plataformas de mídia social como Instagram, Facebook e WhatsApp, essas plataformas são cruciais para a promoção de negócios. Use conteúdo interativo, canais de atendimento ao cliente e publicidade direcionada para ter conversas diretas com seus clientes.
- Localize seu conteúdo: Certifique-se de que seus materiais de marketing estejam em português e sejam culturalmente relevantes.
A localização vai além da tradução do idioma; ela envolve a adaptação do seu conteúdo para que ele se identifique com os valores, o humor e as tradições brasileiras. - Oportunidades de comércio eletrônico: O mercado de comércio eletrônico do Brasil está crescendo rapidamente, apresentando oportunidades de expansão on-line para as empresas.
Invista em um site de fácil utilização, em um aplicativo móvel e em um gateway de pagamento seguro para atender aos consumidores brasileiros que entendem de tecnologia.
Conclusão
Abrir uma empresa no Brasil requer um planejamento cuidadoso, um profundo conhecimento do mercado e adaptabilidade ao ambiente de negócios local.
Cada etapa é essencial para o sucesso, desde a definição da melhor estrutura corporativa até a negociação das nuances das regulamentações brasileiras.
Ao utilizar este guia, realizar pesquisas completas e buscar conhecimento local, você pode construir uma base sólida para o seu negócio no Brasil.
Aproveite as oportunidades que esse mercado vibrante oferece e dê o próximo passo para que você concretize suas ambições empresariais.

